The market for fortified milk is flourishing throughout the world. According to a report, the market share of fortified milk and milk-based products will be valued at 110 billion U.S. dollars in 2022 (1). The wide utilization of Fortified milk is due to its nutritional benefits. However, you might be wondering what is fortified milk? Its benefits, possible downsides, and how it is different from unfortified milk.
This article will answer everything you should know before buying fortified milk from the market.
What is Fortified milk: An introduction
The term fortification is used for a process in which micronutrients, like vitamins and minerals, are added to the food that initially lacks them (2). The aim of fortification is to reduce the common deficiencies of nutrients in the diet, thus avoiding the prevalence of diseases.
Similarly, fortified milk (i.e., cow milk) contains additional vitamins and minerals that are naturally absent in milk. An insignificant quantity of added nutrients may already be present in milk (3).
Milk can be fortified with vitamins like A and D and minerals, including iron, zinc, and folic acid.
However, the choice of the added nutrient is generally based on your location and common deficiencies in your country’s typical diet. For instance, Vitamin A and D fortified milk are commonly available in the United States (4).
Naturally, some vitamins are also present in the milk, but these can be lost during processing. Especially fat-free or skim milk can lose vitamin A and D content due to the removal of fat. This highlights the importance of fortified milk.
It should be noted that the utilization of fortified milk is similar to unfortified milk.
How is fortified milk made?
Generally, milk can be fortified easily. All the vitamins and minerals are available in their dry or powder form. Similarly, nutrients like fat-soluble vitamins are also available in the oily form (5).
In the dairy industry, the fortification method of milk depends on the choices and availability of necessary equipment. But there are two crucial points to consider:
- Homogenizer is required for oily form or oily vitamins
- A dry mixing facility is required for using powdered vitamins or minerals.
Similarly, milk powder can be fortified by blending along with vitamin or mineral powder. Moreover, powdered milk can be fortified with oily vitamins by mixing it with liquid milk before the drying process.
Mostly, the absorbable and active forms of nutrients are used for fortification. For instance, vitamin D3 and vitamin A palmitate is used for the fortification of milk (3).
Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D) forms are heat stable; therefore, they can be added to milk before homogenization and thermal processing (i.e., pasteurization) (6). However, vitamins or minerals which can be destroyed through heat treatment should be added after pasteurization.
Difference between fortified and unfortified milk
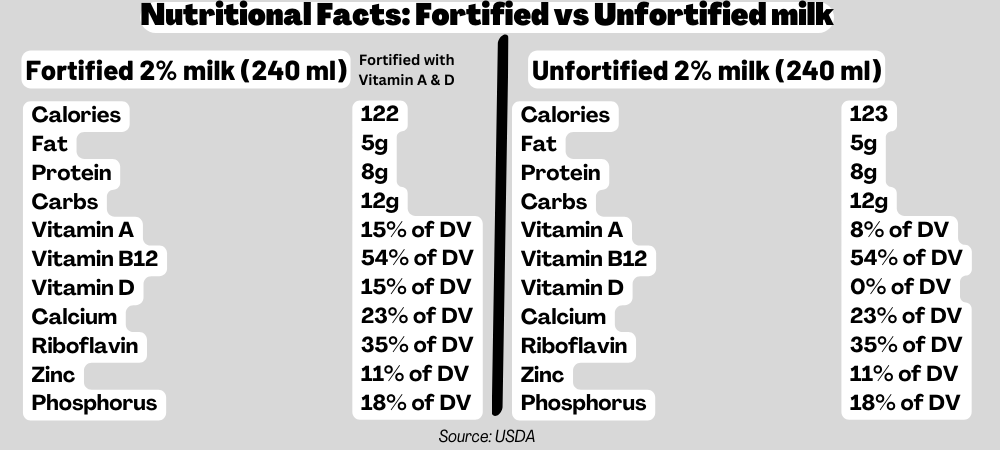
Naturally, unfortified milk is a rich source of carbohydrates, protein, calcium, and various vitamins and minerals. However, fortified milk has vitamins A and D in considerably good quantity. Since fortified milk is added with specific nutrients, its nutritional value for those nutrients increases compared to unfortified milk.
For example, 240 mL of fortified 2% milk contains (3):
- Vitamin A: 15% of Daily Value
- Vitamin D: 15% of Daily Value
On the other hand, 240 mL of unfortified 2% milk contains (3):
- Vitamin A: 8% of Daily Value
- Vitamin D: 0% of Daily value.
Other nutritional contents like caloric value, protein, fat, carbohydrates, other vitamins, and minerals remain the same for both milk types. However, they can vary in fortified milk if any other specific nutrient is added.
Top 10 Benefits of fortified milk
- Naturally, milk has a high content of calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for improving bone health. Hence, both fortified and unfortified milk provide the nutrients that are needed to develop and strengthen human bones (7).
- Consumption of calcium also helps prevent diseases like osteoporosis.
- Vitamin D-fortified milk is traditionally used to prevent diseases like rickets, which are caused by vitamin D deficiency and related to bone weakness (8).
- Fortified milk also provides nutrients to build immunity.
- According to scientific research, countries with wide adoption of fortified milk have a population with higher vitamin D levels in their blood as compared to countries where fortified milk is not used (9).
- Vitamin D also plays a role in the creation of bones by assisting calcium absorption and bone mineralization.
- Milk also provides high-quality protein, which is needed for normal body functioning and muscle building.
- Iron deficiency is a common problem in developing countries. Children with iron deficiency can develop anemia. Iron-fortified milk can help solve this issue.
- Similarly, folic acid deficiency can also be prevented through fortification. In a study, it has been found that multi-nutrient (iron, zinc, Vitamin A) fortified milk can be beneficial for children (up to 3 years) to prevent anemia, especially in developing countries (10).
- Micronutrient-fortified milk also has the ability to enhance the brain health of children, increasing their academic performance as well as learning strategies (11).
Precautions before consuming fortified milk
Lactose, a type of sugar, is specifically found in milk and dairy products. Many people around the world don’t have the ability to digest lactose. This inability to digest is known as lactose intolerance. Also, it may lead to diarrhea, bloating, and other digestive issues after consuming milk or dairy-based products.
If you are lactose intolerant, avoid the consumption of fortified milk. But you can still consume lactose-free products. Moreover, lactose intolerants can consume low-lactose cheeses if they are cheese lovers.
Alternatively, non-dairy foods like soy milk and almond milk can be utilized instead of regular or fortified milk. Such non-dairy products are also fortified to enhance quality and nutritional content.
In addition, if you are allergic to milk, you should not consume any dairy products. People may be allergic to dairy protein, especially casein.
Summary
Fortified milk contains additional nutrients like vitamins and minerals. Commonly, milk is fortified with vitamins A and D. However, the specific nutrient needed to fortify varies depending on the typical diet of the specific population.
Fortifying the milk helps in preventing various nutrient deficiencies, increasing bone health, and avoiding diseases like rickets and anemia.
Despite the many benefits of fortified milk, you must restrict yourself from its consumption if you are lactose intolerant. In case of milk allergy, avoid the intake of dairy-based products.
Otherwise, you can easily purchase fortified milk from the market. Read the label to know if it is fortified or not. Don’t forget to read the “nutritional facts” label before buying.